Deep Learning Book Series 3.4 and 3.5 Marginal and Conditional Probability
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series 3.1 to 3.3 Probability Mass and Density Functions
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Preprocessing for deep learning: from covariance matrix to image whitening
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.12 Example Principal Components Analysis
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.11 The determinant
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.10 The Trace Operator
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.9 The Moore Penrose Pseudoinverse
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.8 Singular Value Decomposition
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.7 Eigendecomposition
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.6 Special Kinds of Matrices and Vectors
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.5 Norms
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.4 Linear Dependence and Span
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.3 Identity and Inverse Matrices
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.2 Multiplying Matrices and Vectors
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · 2.1 Scalars Vectors Matrices and Tensors
⥈ ⥈ ⥈Deep Learning Book Series · Introduction
⥈ ⥈ ⥈
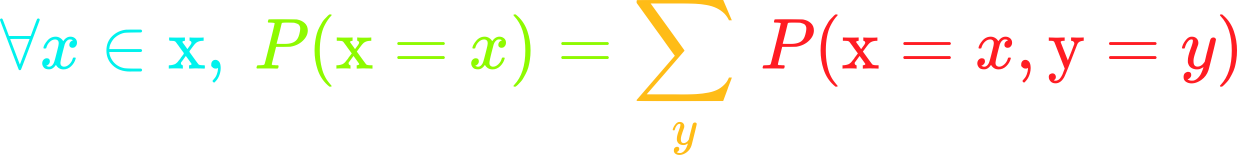 The sum rule allows to calculate marginal probability from joint probability.
The sum rule allows to calculate marginal probability from joint probability. 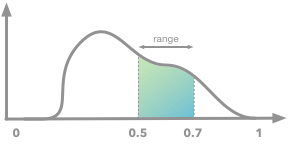 Probability density function and area under the curve between 0.5 and 0.7.
Probability density function and area under the curve between 0.5 and 0.7. 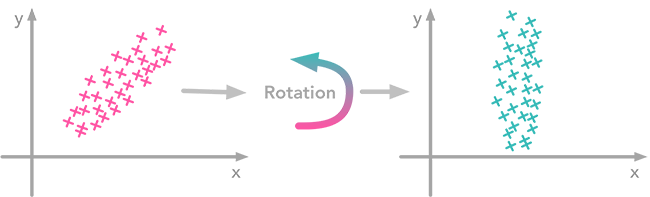 The left plot shows correlated data. For instance, if you take a data point with a big $x$ value, chances are that $y$ will also be quite big. Now take all data points and do a rotation (maybe around 45 degrees counterclockwise): the new data (plotted on the right) is not correlated anymore.
The left plot shows correlated data. For instance, if you take a data point with a big $x$ value, chances are that $y$ will also be quite big. Now take all data points and do a rotation (maybe around 45 degrees counterclockwise): the new data (plotted on the right) is not correlated anymore. 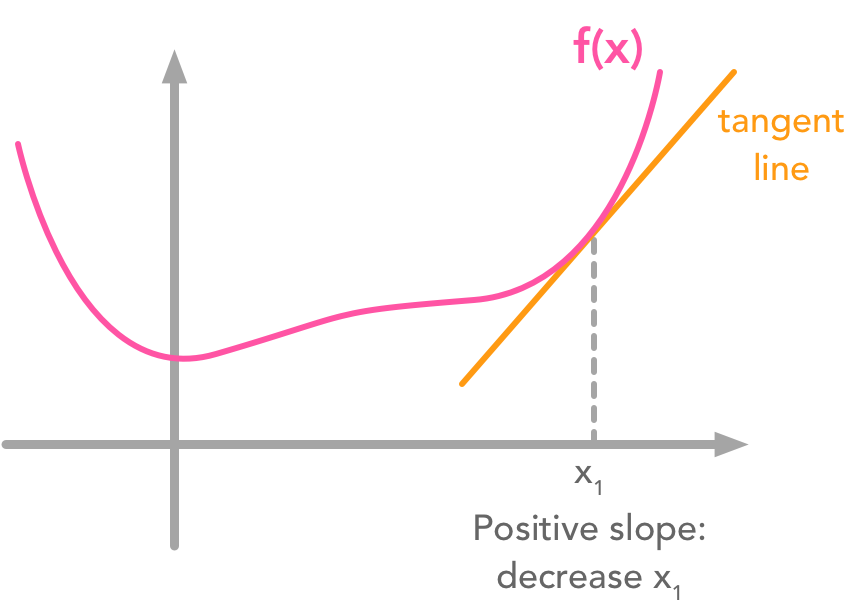 Gradient descent
Gradient descent 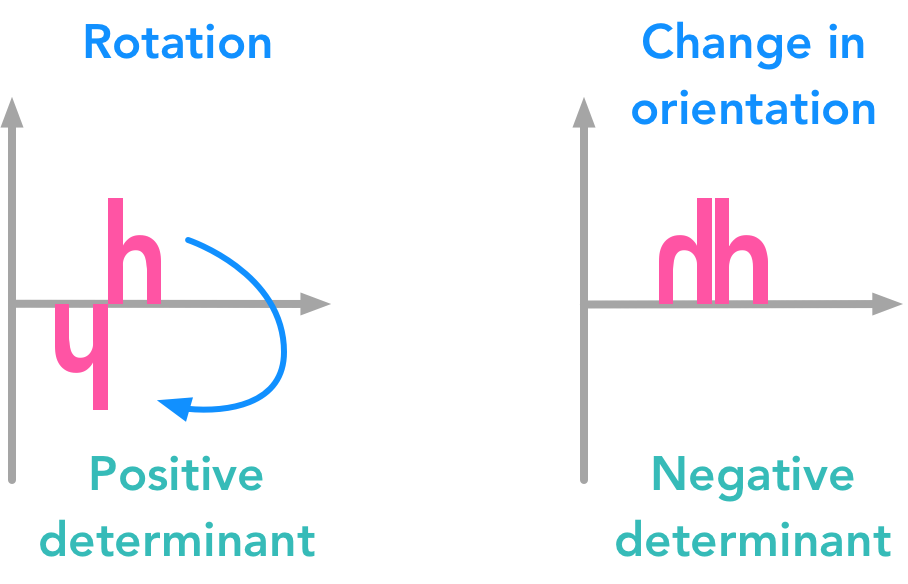 The determinant of a matrix can tell you a lot of things about the transformation associated with this matrix
The determinant of a matrix can tell you a lot of things about the transformation associated with this matrix 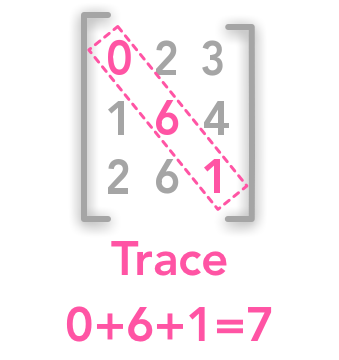 The trace of matrix
The trace of matrix 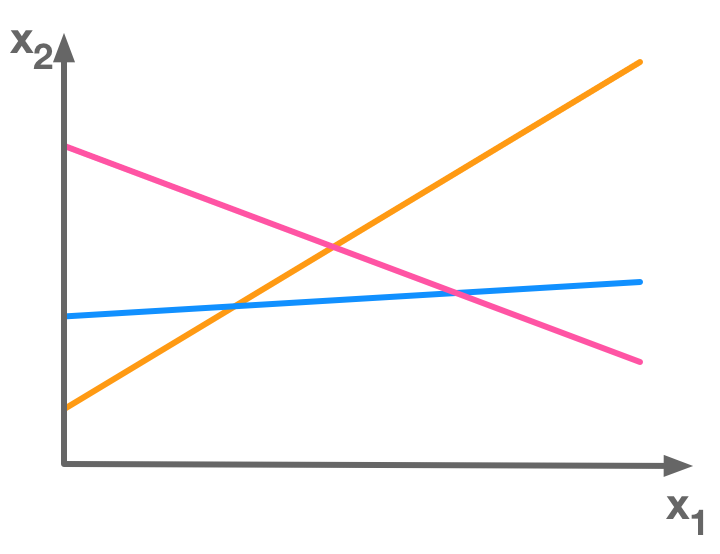 There is more equations (3) than unknowns (2) so this is an overdetermined system of equations
There is more equations (3) than unknowns (2) so this is an overdetermined system of equations 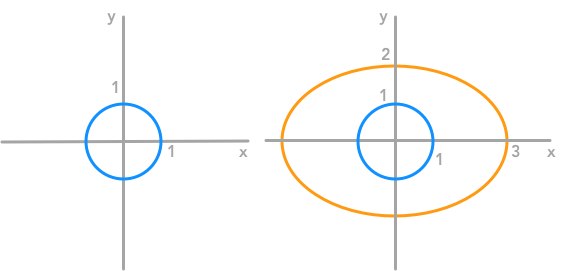 The unit circle and its transformation by a matrix
The unit circle and its transformation by a matrix 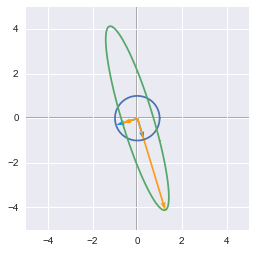 The unit circle and its transformation by the matrix A. The vectors are the eigenvectors of A.
The unit circle and its transformation by the matrix A. The vectors are the eigenvectors of A. 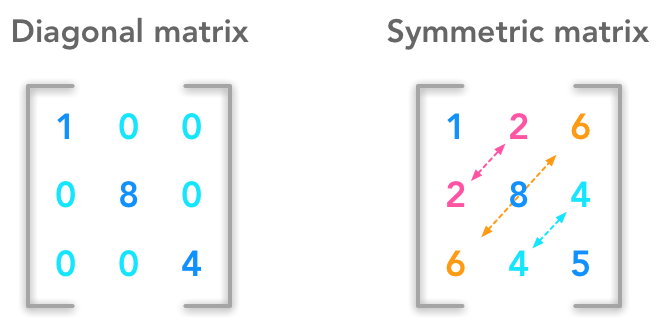 Example of diagonal and symmetric matrices
Example of diagonal and symmetric matrices 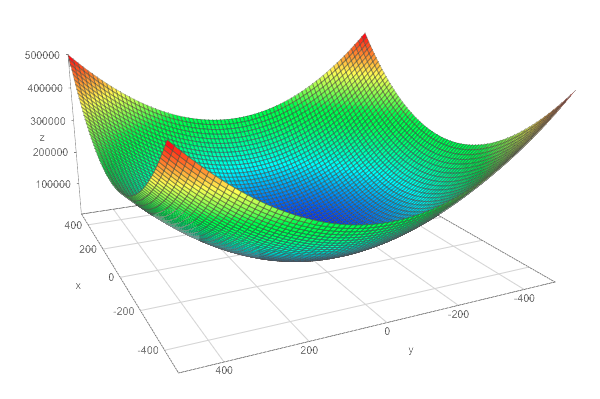 The squared L2 norm
The squared L2 norm 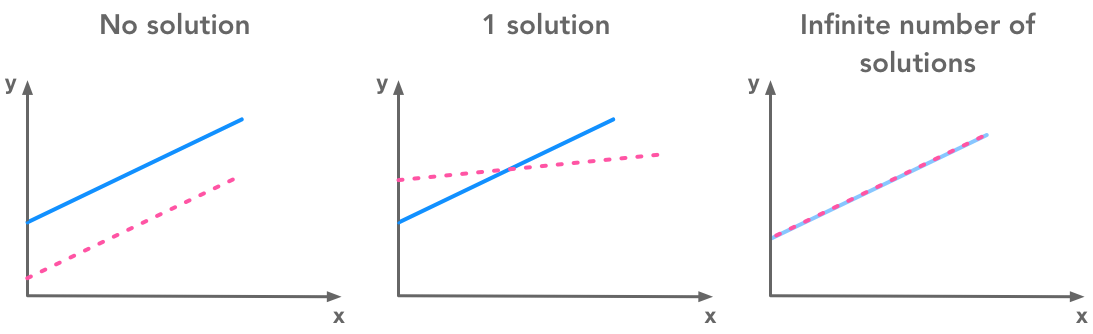 A system of equations has no solution, 1 solution or an infinite number of solutions
A system of equations has no solution, 1 solution or an infinite number of solutions 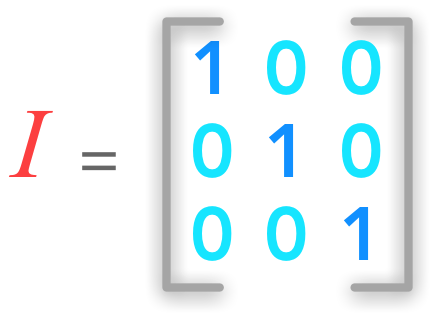 A 3 by 3 identity matrix
A 3 by 3 identity matrix 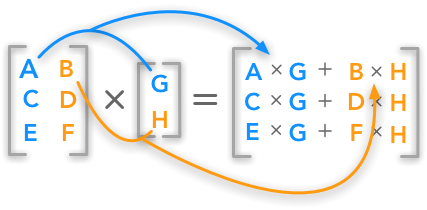 The dot product between a matrix and a vector
The dot product between a matrix and a vector 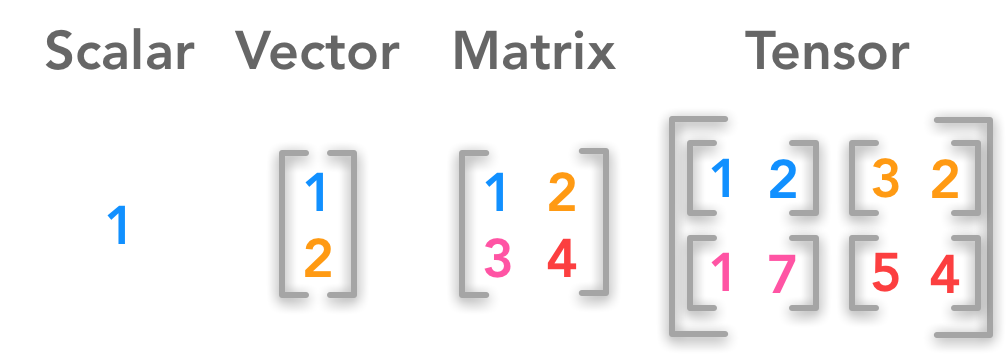 Difference between a scalar, a vector, a matrix and a tensor
Difference between a scalar, a vector, a matrix and a tensor  The Deep Learning Book - Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., and Courville, A. (2016)
The Deep Learning Book - Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., and Courville, A. (2016)